Fat32 Formatter on 32-bit and 64-bit PCs. This download is licensed as freeware for the Windows (32-bit and 64-bit) operating system on a laptop or desktop PC from hard drive formatters without restrictions. Fat32 Formatter 1.1 is available to all software users as a free download for Windows 10 PCs but also without a hitch on Windows 7. The partition size maximum for FAT32 is 16TB. Microsoft workbook laptop. The drive size limit for MBR is 2TB. There is an artificial limit of 32 GB placed on FAT32 by Windows, but not a limit of FAT32 itself. In regards to the UEFI specification, it states that UEFI must be able to boot from FAT32. Jun 22, 2020 FAT32 Format is a free program that enables people to configure any hard drive, micro SD card, SD card, and USB drive that is more than 32 GB to the FAT32 file system. Microsoft Windows operating systems are notorious for not being able to structure a drive that is higher than 32 GB. The good thing with FAT is that the data stored under this format is universally readable by any Windows PC, no matter it is DOS, Windows 2000, or Windows XP. FAT32 file system. As the hard drive capacity goes beyond 2 GB, FAT32 was introduced in rush to allow for larger partitions and less waste, however Microsoft did not have enough foresight. FAT32 Format is a simple, fast program for formatting hard drives and other storage media to the FAT32 format. FAT32 Format is an aptly named tool that can format a storage device in the FAT32 file system. This version is designed specifically for the Windows 2000, XP, and Vista operating systems and will not work with newer versions, such as.
-->Fat 32 Format Windows 10
Applies to: Windows 10, Windows Server 2016
Formats a disk to accept Windows files. You must be a member of the Administrators group to format a hard drive.
Note
You can also use the format command, with different parameters, from the Recovery Console. For more information about the recovery console, see Windows Recovery Environment (Windows RE).
Syntax
Parameters
| Parameter | Description | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Specifies the mount point, volume name, or drive letter (followed by a colon) of the drive that you want to format. If you do not specify any of the following command-line options, format uses the volume type to determine the default format for the disk. | ||
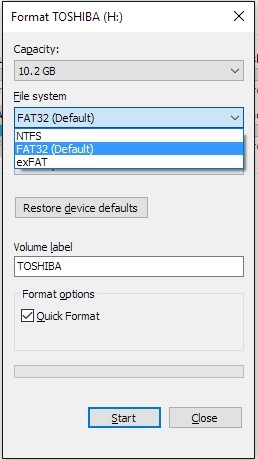
| /fs:{FAT | FAT32 | NTFS} | Specifies the type of file system (FAT, FAT32, NTFS). |
/v: | Specifies the volume label. If you omit the /v command-line option or use it without specifying a volume label, format prompts you for the volume label after the formatting is complete. Use the syntax /v: to prevent the prompt for a volume label. If you use a single format command to format more than one disk, all of the disks will be given the same volume label. | ||
/a: | Specifies the allocation unit size to use on FAT, FAT32, or NTFS volumes. If you don't specify unitsize, it's chosen based on volume size. Default settings are strongly recommended for general use. The following list presents valid values for NTFS, FAT, and FAT32 unitsize:
| ||
| /q | Performs a quick format. Deletes the file table and the root directory of a previously formatted volume, but does not perform a sector-by-sector scan for bad areas. You should use the /q command-line option to format only previously formatted volumes that you know are in good condition. Note that /q overrides /p. | ||
/f: | Specifies the size of the floppy disk to format. When possible, use this command-line option instead of the /t and /n command-line options. Windows accepts the following values for size:
| ||
/t: | Specifies the number of tracks on the disk. When possible, use the /f command-line option instead. If you use the /t option, you must also use the /n option. These options together provide an alternative method of specifying the size of the disk that is being formatted. This option is not valid with the /f option. | ||
/n: | Specifies the number of sectors per track. When possible, use the /f command-line option instead of /n. If you use /n, you must also use /t. These two options together provide an alternative method of specifying the size of the disk that is being formatted. This option is not valid with the /f option. | ||
/p: | Zeros every sector on the volume for the number of passes specified. This option is not valid with the /q option. | ||
| /c | NTFS only. Files created on the new volume will be compressed by default. | ||
| /x | Causes the volume to dismount, if necessary, before it's formatted. Any open handles to the volume will no longer be valid. | ||
| /? | Displays help at the command prompt. |
Remarks
The format command creates a new root directory and file system for the disk. It can also check for bad areas on the disk, and it can delete all data on the disk. To be able to use a new disk, you must first use this command to format the disk.
After formatting a floppy disk, format displays the following message:
Volume label (11 characters, ENTER for none)?To add a volume label, type up to 11 characters (including spaces). If you do not want to add a volume label to the disk, press ENTER.
When you use the format command to format a hard disk, a warning message similar to the following displays:
To format the hard disk, press Y; if you do not want to format the disk, press N.
FAT file systems restrict the number of clusters to no more than 65526. FAT32 file systems restrict the number of clusters to between 65527 and 4177917.
NTFS compression is not supported for allocation unit sizes above 4096.
Note
Format will immediately stop processing if it determines that the previous requirements can't be met using the specified cluster size.
When formatting is complete, format displays messages that show the total disk space, the spaces marked as defective, and the space available for your files.
You can speed up the formatting process by using the /q command-line option. Use this option only if there are no bad sectors on your hard disk.
You shouldn't use the format command on a drive that was prepared by using the subst command. You can't format disks over a network.
The following table lists each exit code and a brief description of its meaning.
Exit code Description 0 The format operation was successful. 1 Incorrect parameters were supplied. 4 A fatal error occurred (which is any error other than 0, 1, or 5). 5 The user pressed N in response to the prompt 'Proceed with Format (Y/N)?' to stop the process. You can check these exit codes by using the ERRORLEVEL environment variable with the if batch command.
Examples
Fat Formatter Windows 10
To format a new floppy disk in drive A using the default size, type:
Windows Fat Format Download
To perform a quick format operation on a previously formatted floppy disk in drive A, type:
Windows 10 Format Fat Drive
To format a floppy disk in drive A and assign it the volume label DATA, type:

